Sound Theory 101: Energy, Frequency and Vibration

Understanding the Invisible Language of Sound
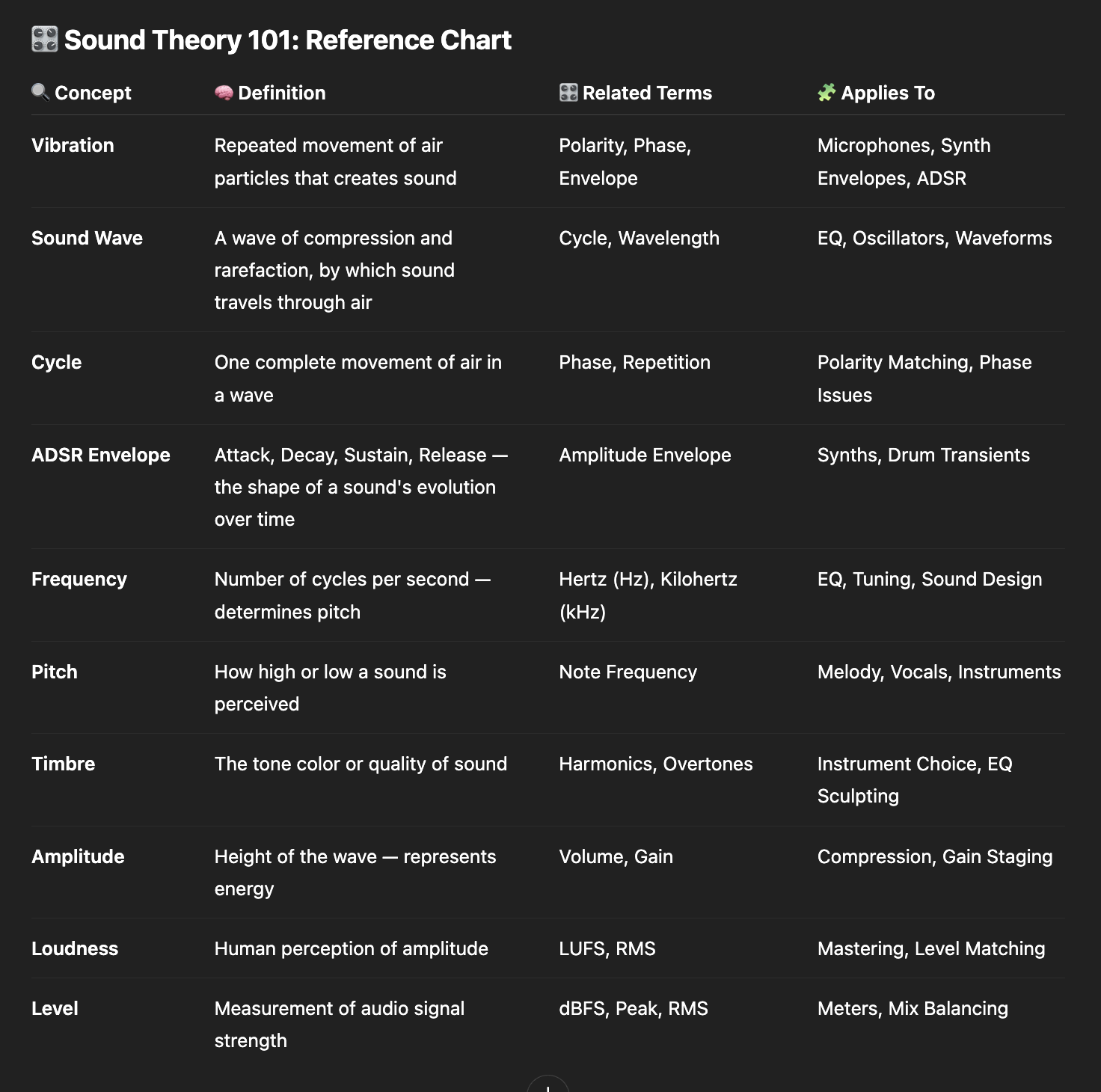
Sound is invisible, but it shapes everything we hear in music. Whether you're EQ’ing a snare, dialing in reverb, or crafting synth patches, you're really working with three forces: vibration, frequency, and energy. These are the physics behind every track, beat, and melody.
Let’s break it down.
🧩 Part 1 – Vibration
What is a sound wave?
Sound begins as vibration—air moving in waves that our ears and microphones pick up.
-
Sound pressure is the result of vibrating objects pushing and pulling air molecules. This creates compressions and rarefactions (dense and loose parts of a wave), which form the sound wave.
-
Cycles refer to how often these waves repeat in a second. This repetition is measured in Hertz (Hz). The more cycles per second, the higher the pitch.
-
Phase and polarity are about where those waves start and how they align. If two waves are out of phase, they can cancel each other out.
-
Envelopes (ADSR) describe how a sound unfolds over time:
-
Attack – how fast it starts
-
Decay – how quickly it drops after the peak
-
Sustain – the level it holds
-
Release – how long it takes to fade out
-
Understanding vibration = understanding shape and motion.
The Cycle of Sound: 6 Ways to Measure Audio Waveforms
 ⭐️ Start by downloading all of my FREE Music Production Guides ⭐️ It took me years to learn this stuff!
⭐️ Start by downloading all of my FREE Music Production Guides ⭐️ It took me years to learn this stuff!
🛠️ Part 2 – Frequency
What makes a sound sound like itself?
This is where frequency steps in—how fast something vibrates.
-
Speed of vibration = Pitch. Low frequencies = bass. High frequencies = treble.
-
Wavelength is the physical space between cycles. Shorter wavelength = higher pitch.
-
Timbre (or tone color) is what makes the same note on a guitar sound different from a piano. It comes from the harmonics layered on top of the fundamental frequency.
So, even if two notes have the same pitch, their unique blend of overtones gives them distinct identities.
What Is Frequency in Music Production?
🎧 Part 3 – Energy
What gives sound its power?
This is where amplitude and loudness live.
-
Amplitude is the height of the wave—how far it pushes the air.
-
Loudness is how we perceive that height. Our ears are more sensitive to mid frequencies, so loudness isn't always linear.
-
Levels refer to how we measure and balance sounds. This is where metering comes in: keeping your levels consistent ensures your track hits right—without clipping or getting buried.
Think of energy as the fuel driving the whole sound wave engine.
What Is a Decibel? dBFS, dBV, dBu and dBSPL Explained in Simple Terms
 ⭐️ Download my FREE Magic EQ Settings that work on EVERYTHING ⭐️
⭐️ Download my FREE Magic EQ Settings that work on EVERYTHING ⭐️
Final Thoughts
Sound is energy in motion.
By understanding vibration, frequency, and amplitude, you gain a deeper control over every element of your mix. These aren’t just abstract science terms—they’re the foundation of creative sound design, vocal production, and every beat you drop.
Want to make your mix feel alive?
Master the movement. 🎛️
⭐️ Download my Free Magic Delay settings Guide ⭐️
⭐️ Download my Free Magic Reverb settings Guide ⭐️
#protools #daw #homestudio #recordingschool #recording #musicproduction
Also read:
How to Start Your Own Online Business Teaching Music

Hey, I'm Futch - Music Production Coach and Ableton Certified Trainer
Learn how to make your first song and beat in Ableton Live with my
FREE 90-minute Ableton Live course
I've been teaching audio engineering and music production for 35 years.⭐️
Check out my new online music production program: Music Production Ninja...








