Classic Drum Machines: The Elektron Machinedrum ⚙️

The Machine That Escaped the Future
The Elektron Machinedrum didn’t sound analog.
It didn’t sound vintage.
It didn’t sound like anything you recognized.
It sounded like the future breaking through a crack in the present.
Where classic drum machines created patterns…
the Machinedrum created worlds.
It wasn’t about imitating drums —
it was about designing new realities of rhythm.
Quick Summary:
👉 Released in 2001, the Elektron Machinedrum used digital modeling, sound design engines, and advanced sequencing to redefine electronic drums, influencing genres from IDM and techno to experimental, glitch, and modern electronic hybrid styles.
⚙️ The History — The Swedish Synthesis Revolution
Question: How did the Machinedrum begin?
In 2001, Swedish company Elektron released the Machinedrum SPS-1, a digital drum computer built not from samples, but from multiple synthesis engines.
This wasn’t nostalgia.
This wasn’t analog revival.
This was a new class of instrument.
Its design language introduced concepts now standard in modern digital hardware:
-
parameter locks
-
deep modulation
-
step-level sound changes
-
per-track synthesis machines
-
futuristic sequencing philosophies
Elektron wasn’t competing with Roland or Akai.
They were writing a new chapter.
🎯 Core Innovations
-
Multiple digital synthesis engines (TRX, EFM, PI, GND, and more).
-
Parameter Locks — change any parameter on any step.
-
LFO madness — modulation on nearly everything.
-
Real-time performance controls — knobs, scenes, morphing.
-
Polyphonic, multi-timbral sequencing — incredibly advanced for 2001.
“The Machinedrum wasn’t a drum machine.
It was a sound design instrument disguised as one.”
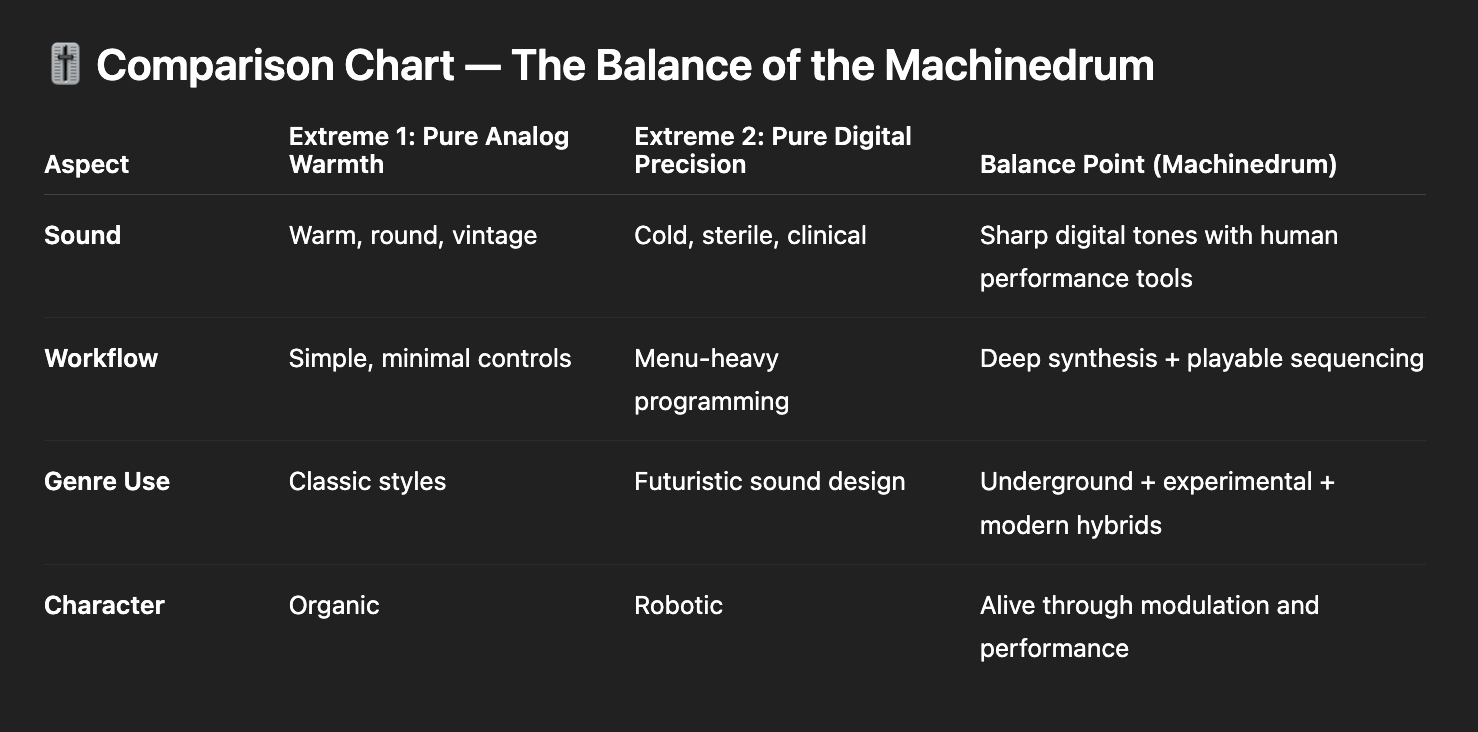
🧩 Balance Point
Between precision and chaos.
Between structure and surprise.
The machine rewarded control — and encouraged exploration.
🔑 Key Takeaway
The Machinedrum broke the definition of ‘drum machine’ and created a new one.
🔊 The Originality — Digital, Alien, Alive
Question: What makes the Machinedrum’s sound unique?
It wasn’t analog.
It wasn’t sample-based.
It was something entirely different:
digital synthesis with human hands.
The Machinedrum’s engines could generate:
-
metallic hits
-
synthetic thumps
-
glitch percussion
-
FM clatter
-
noisy textures
-
futuristic toms
-
alien snares
-
polyrhythmic pulses
-
percussive tone sculptures
The sound was sharp, hybrid, and endlessly programmable.
🎯 Core Sound Traits
-
Digital punch — clear, sharp, cutting.
-
Glitch-forward percussion — IDM-ready.
-
FM tones — clangy, aggressive, expressive.
-
Evolving textures — thanks to LFOs and parameter locks.
-
Machine layering — blend multiple engines into one hit.
“The Machinedrum sounded like the inside of a computer dreaming.”
🧩 Balance Point
Between mathematical and organic.
It could sound cold.
It could sound alive.
The difference was you.
🔑 Key Takeaway
The Machinedrum’s originality lives in its depth — limitless rhythm sculpting.
🌍 The Cultural Impact — The Machine of the Underground
The Machinedrum became a secret weapon for producers who wanted rhythms that didn’t sound like anyone else’s.
It didn’t dominate radio.
It dominated innovation.
 ⭐️ Download my Free Guide The Magic EQ Settings that work on EVERYTHING!
⭐️ Download my Free Guide The Magic EQ Settings that work on EVERYTHING!
🎛️ IDM / Experimental — The Frontier Sound
The Machinedrum became iconic in experimental, glitch, and IDM.
Key Artists
-
Autechre
-
Squarepusher
-
Richard Devine
-
Jimmy Edgar
-
Clark
It was embraced by the producers who treated rhythm as sculpture.
🔊 Techno / Industrial — The Engine of Motion
Techno artists loved it for its precision, aggression, and tweakability.
Key Artists
-
Surgeon
-
Blawan
-
Speedy J
-
Monolake
The 909 may be the heart of techno — but the Machinedrum became its mind.
🎹 Electronic & Pop — The Texture Tool
A number of adventurous producers used the Machinedrum for layering and texture creation:
-
The Knife
-
Modeselektor
-
Depeche Mode (later sessions)
-
Bon Iver (post-processing and glitch elements)
It became a sound-design companion to synth-heavy production.
The Knife "Silent Shout" (Official Music Video)
🧩 Balance Point
Between club functionality and sound-art experimentation.
No other drum machine sits so comfortably across both extremes.
🔑 Key Takeaway
The Machinedrum gave rhythm a new vocabulary — strange, digital, limitless.
🧠 FAQ
Q: What year was the Machinedrum released?
A: 2001 (and updated versions continued through the 2010s).
Q: What type of sounds does the Machinedrum generate?
A: Digital drum synthesis — FM, metallic, glitch, percussion modeling, and hybrid tones.
Q: Is the Machinedrum analog or digital?
A: Fully digital, with multiple synthesis engines.
Q: Why is the Machinedrum influential?
A: It introduced parameter locks, deep sequencing, and performance features that shaped modern hardware design.
 ⭐️ Start by downloading all of my FREE Music Production Guides ⭐️ It took me years to learn this stuff!
⭐️ Start by downloading all of my FREE Music Production Guides ⭐️ It took me years to learn this stuff!
🔑 Why This Matters
The Elektron Machinedrum didn’t follow in the footsteps of classic drum machines —
it redefined what a drum machine could be.
It gave producers:
-
rhythm as design
-
sound as sculpture
-
performance as expression
“The Machinedrum wasn’t the future of drums.
It was the future of imagination.”
⭐️ Download my Free Magic Delay settings Guide ⭐️
⭐️ Download my Free Magic Reverb settings Guide ⭐️
#protools #daw #homestudio #recordingschool #recording #musicproduction
Also read:
How to Start Your Own Online Business Teaching Music

Hey, I'm Futch - Music Production Coach and Ableton Certified Trainer
Learn how to make your first song and beat in Ableton Live with my
FREE 90-minute Ableton Live course
I've been teaching audio engineering and music production for 35 years.⭐️
Check out my new online music production program: Music Production Ninja...








